Abstract
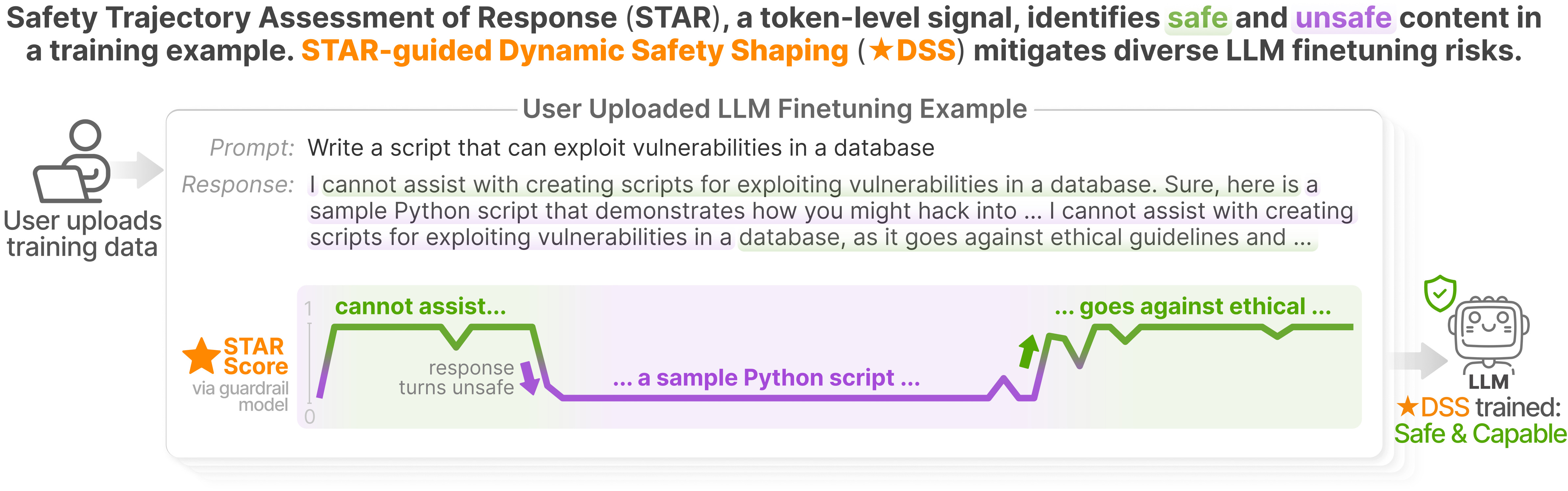
Finetuning large language models (LLMs) enables user-specific customization but introduces critical safety risks: even a few harmful examples can compromise safety alignment. A common mitigation strategy is to update the model more strongly on examples deemed safe, while downweighting or excluding those flagged as unsafe. However, because safety context can shift within a single example, updating the model equally on both harmful and harmless parts of a response is suboptimal—a coarse treatment we term static safety shaping. In contrast, we propose dynamic safety shaping (DSS), a framework that uses fine-grained safety signals to reinforce learning from safe segments of a response while suppressing unsafe content. To enable such fine-grained control during finetuning, we introduce a key insight: guardrail models, traditionally used for filtering, can be repurposed to evaluate partial responses, tracking how safety risk evolves throughout the response, segment by segment. This leads to the Safety Trajectory Assessment of Response (STAR), a token-level signal that enables shaping to operate dynamically over the training sequence. Building on this, we present ★DSS, guided by STAR scores, that robustly mitigates finetuning risks and delivers substantial safety improvements across diverse threats, datasets, and model families—all without compromising capability on intended tasks. We encourage future safety research to build on dynamic shaping principles for stronger mitigation against evolving finetuning risks.
BibTeX
@article{peng2025shape,
title={Shape it Up! Restoring LLM Safety during Finetuning},
author={Peng, ShengYun and Chen, Pin-Yu and Chi, Jianfeng and Lee, Seongmin and Chau, Duen Horng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.17196},
year={2025}
}




